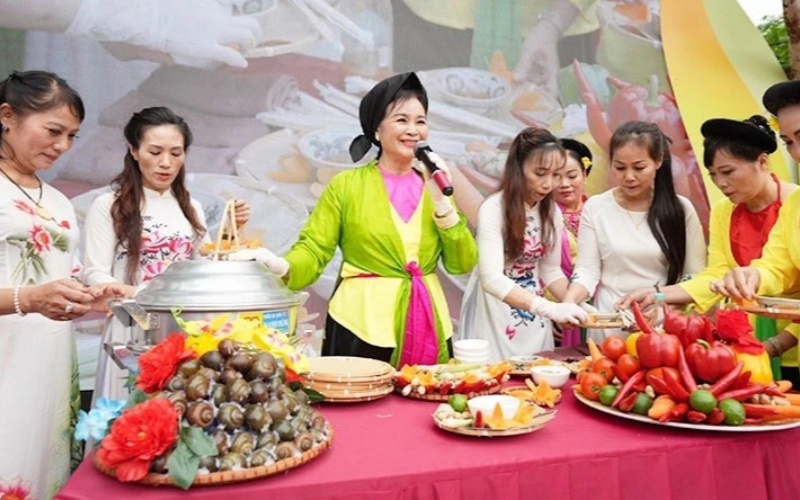
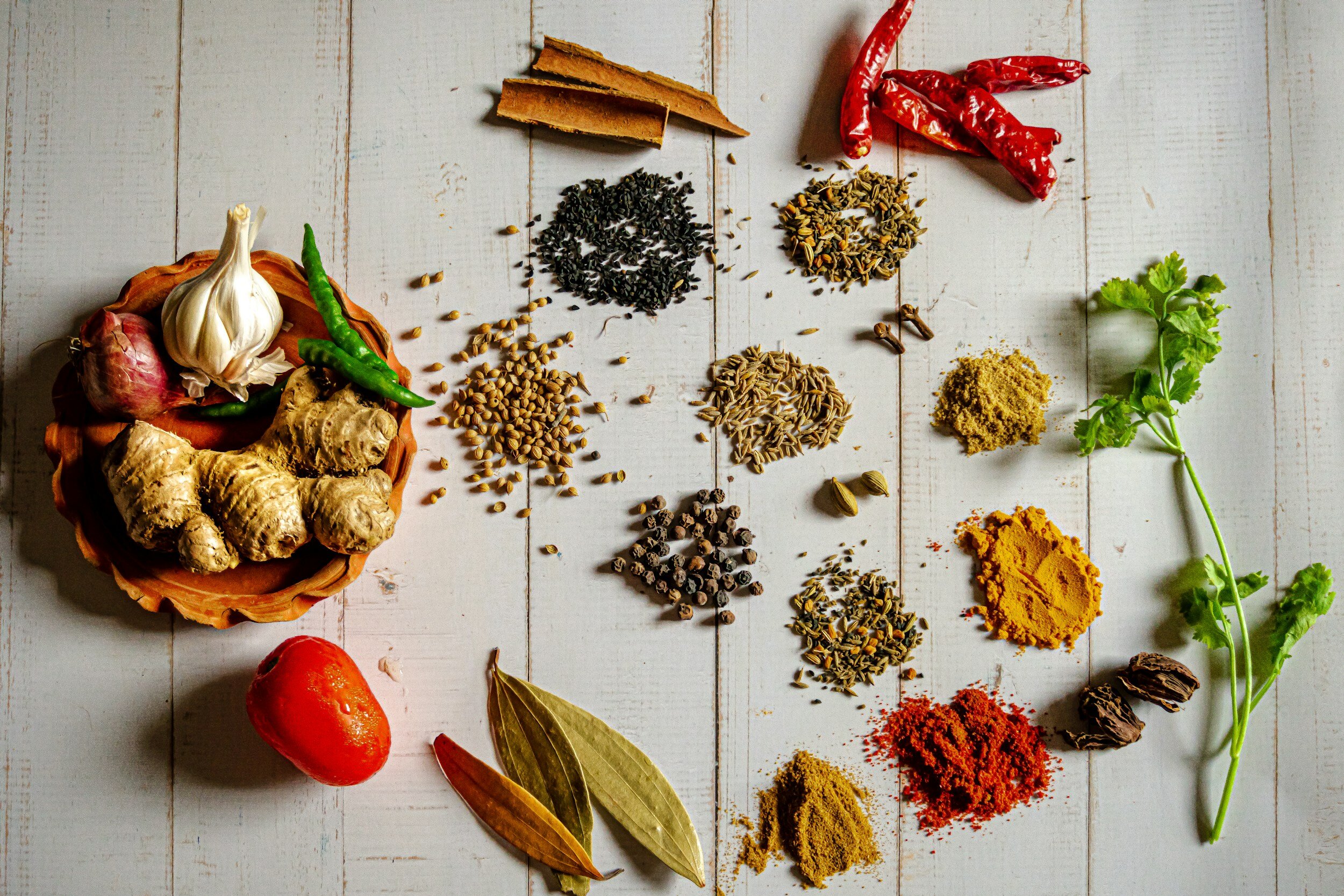
1. Celebrations and Rituals: Food plays a central role in cultural celebrations and rituals. Traditional dishes are often prepared during holidays, weddings, and festivals, symbolizing community and shared heritage. For example, Thanksgiving in the United States centers around a feast featuring turkey, stuffing, and pumpkin pie, while Diwali in India celebrates with sweets and savory snacks.
2. Family Traditions: Family recipes are often passed down through generations, preserving cultural heritage and fostering a sense of belonging. Cooking together can strengthen family bonds and create lasting memories. Many cultures emphasize communal dining, where sharing food enhances social connections.
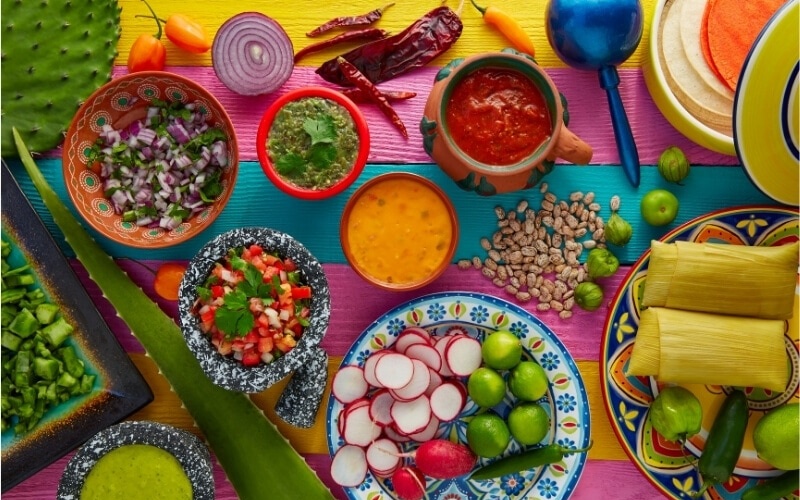

3. Regional Ingredients: Local ingredients and climate influence culinary traditions. For instance, Mediterranean cuisine features olive oil, fresh vegetables, and seafood, while hearty stews and root vegetables are common in colder regions. Understanding the connection between geography and food can enhance our appreciation for different cuisines.
4. Culinary Fusion: Globalization has led to the blending of culinary traditions, resulting in fusion cuisine. This creative approach combines elements from different cultures, leading to unique dishes that celebrate diversity. Examples include sushi burritos and Korean tacos, showcasing the beauty of culinary innovation.
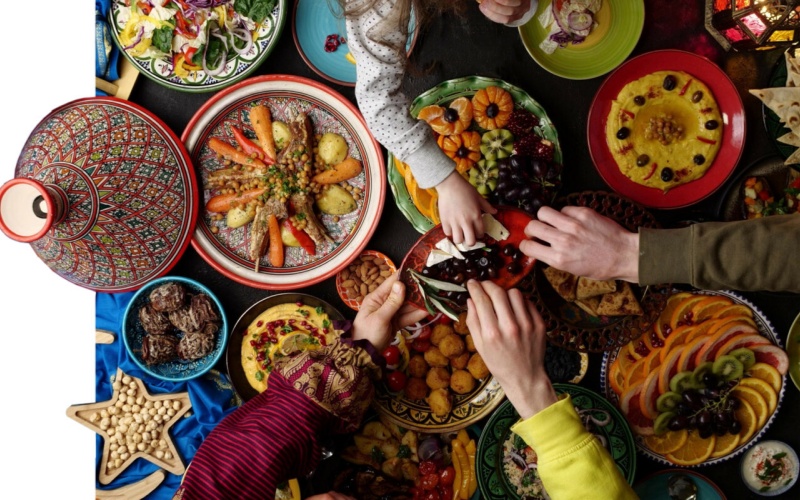

5. Food as a Narrative: Food can tell stories about a culture’s history, values, and struggles. Dishes often reflect the influences of migration, trade, and colonization. Exploring the narratives behind traditional foods can deepen our understanding of cultural identity and resilience.
In conclusion, food is a powerful expression of culture, connecting people across generations and geographies. By exploring culinary traditions, we can celebrate diversity, foster understanding, and appreciate the rich tapestry of human experience.